Choosing a health insurance plan can feel overwhelming, especially when you're staring at acronyms like PPO and HMO with no clear explanation of what actually matters. These two plan types dominate the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace, employer-sponsored coverage, and private insurance — and choosing the wrong one can cost you thousands of dollars per year or lock you into a frustrating care experience.
This guide breaks it down clearly, without insurance jargon or sales fluff.
By the end of this article, you'll know:
- What PPO and HMO actually mean
- How they differ in cost, flexibility, and access to doctors
- Which plan type makes sense for different situations
- How ACA subsidies can change the math entirely
What Is an HMO Health Insurance Plan?
HMO stands for Health Maintenance Organization.
An HMO plan is built around cost control and coordination of care. It does this by limiting where you can go for care and requiring a central doctor to manage your treatment.
Key Characteristics of HMO Plans
- You must choose a Primary Care Physician (PCP)
- Your PCP controls referrals to specialists
- Care is limited to an in-network provider network
- Out-of-network care is generally not covered (except emergencies)
- Monthly premiums are usually lower
- Predictable costs and fewer surprise bills
HMOs are designed to be simple, affordable, and structured — but that structure can feel restrictive if you value flexibility.

What Is a PPO Health Insurance Plan?
PPO stands for Preferred Provider Organization.
A PPO plan prioritizes freedom of choice. You can see specialists without referrals, visit doctors outside the network, and manage your care more independently.
Key Characteristics of PPO Plans
- No Primary Care Physician required
- No referrals needed for specialists
- You can use out-of-network providers (at higher cost)
- Larger provider networks
- Higher monthly premiums
- Higher deductibles and cost-sharing
PPOs are popular with people who want control over their healthcare decisions — but that freedom comes at a price.
PPO vs HMO: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Premium | Lower | Higher |
| PCP Required | Yes | No |
| Specialist Referrals | Required | Not required |
| Out-of-Network Coverage | No (except emergencies) | Yes |
| Provider Network | Smaller | Larger |
| Cost Predictability | High | Lower |
| Flexibility | Limited | High |
This table summarizes the trade-off clearly: HMOs save money, PPOs buy freedom.
Cost Differences: Why PPO Plans Cost More
The biggest reason PPO plans cost more is risk — for the insurer.
PPO plans:
- Allow patients to self-direct care
- Permit out-of-network usage
- Encourage specialist visits without gatekeeping
That flexibility increases utilization and unpredictable claims, which drives premiums up.
HMO plans:
- Control utilization through PCPs
- Negotiate tighter contracts with providers
- Reduce unnecessary specialist care
The result: HMOs are cheaper, PPOs are more expensive, even before deductibles and copays enter the picture.

Networks: Why This Matters More Than People Realize
Your plan's provider network determines which doctors, hospitals, labs, and specialists you can use.
HMO Networks
- Narrower and more localized
- Often centered around hospital systems
- Limited rural or multi-state access
- Better pricing consistency
PPO Networks
- Larger and more national
- Better for travelers or multi-state workers
- More specialists available
- Greater variability in costs
If you already have doctors you want to keep, network compatibility should be checked before choosing a plan — not after.
Referrals and Care Management
This is where many people get frustrated with HMOs.
HMO Referral System
- PCP is your gatekeeper
- Specialist visits require approval
- Delays can occur
- Care is more coordinated
PPO Referral Freedom
- Self-refer to specialists
- Faster access to care
- More control over treatment decisions
- Less centralized coordination
There's no universally "better" system — it depends on how you use healthcare.
Out-of-Network Coverage: A Critical Difference
This is one of the most misunderstood areas of health insurance.
HMO Plans
- No coverage outside the network
- Emergency care only
- Non-emergency out-of-network bills = 100% your responsibility
PPO Plans
- Partial coverage out of network
- Higher deductibles and coinsurance
- Balance billing risk still exists
If you travel frequently, live near state borders, or see specialized providers, this difference alone may justify a PPO.
PPO vs HMO on the ACA Marketplace
Under the ACA, both PPO and HMO plans are available — but availability varies by state and ZIP code.
In many states:
- HMOs dominate the marketplace
- PPO options are limited or regional
- PPO premiums are significantly higher
This makes subsidies extremely important when comparing plans.
Learn more about how subsidies are calculated to understand your real costs.
How ACA Subsidies Change the PPO vs HMO Decision
ACA subsidies (premium tax credits) are based on:
- Your household income
- Federal Poverty Level (FPL)
- Local benchmark Silver plan pricing
In some cases:
- An HMO may cost $0/month
- A PPO may become affordable after subsidies
- The price gap narrows dramatically
This is why comparing plans without subsidies is misleading.
Check your eligibility:
See Your Real Costs After Subsidies
Use our free ACA Subsidy Calculator to compare PPO and HMO plans based on your actual out-of-pocket costs.
Calculate Your Subsidy →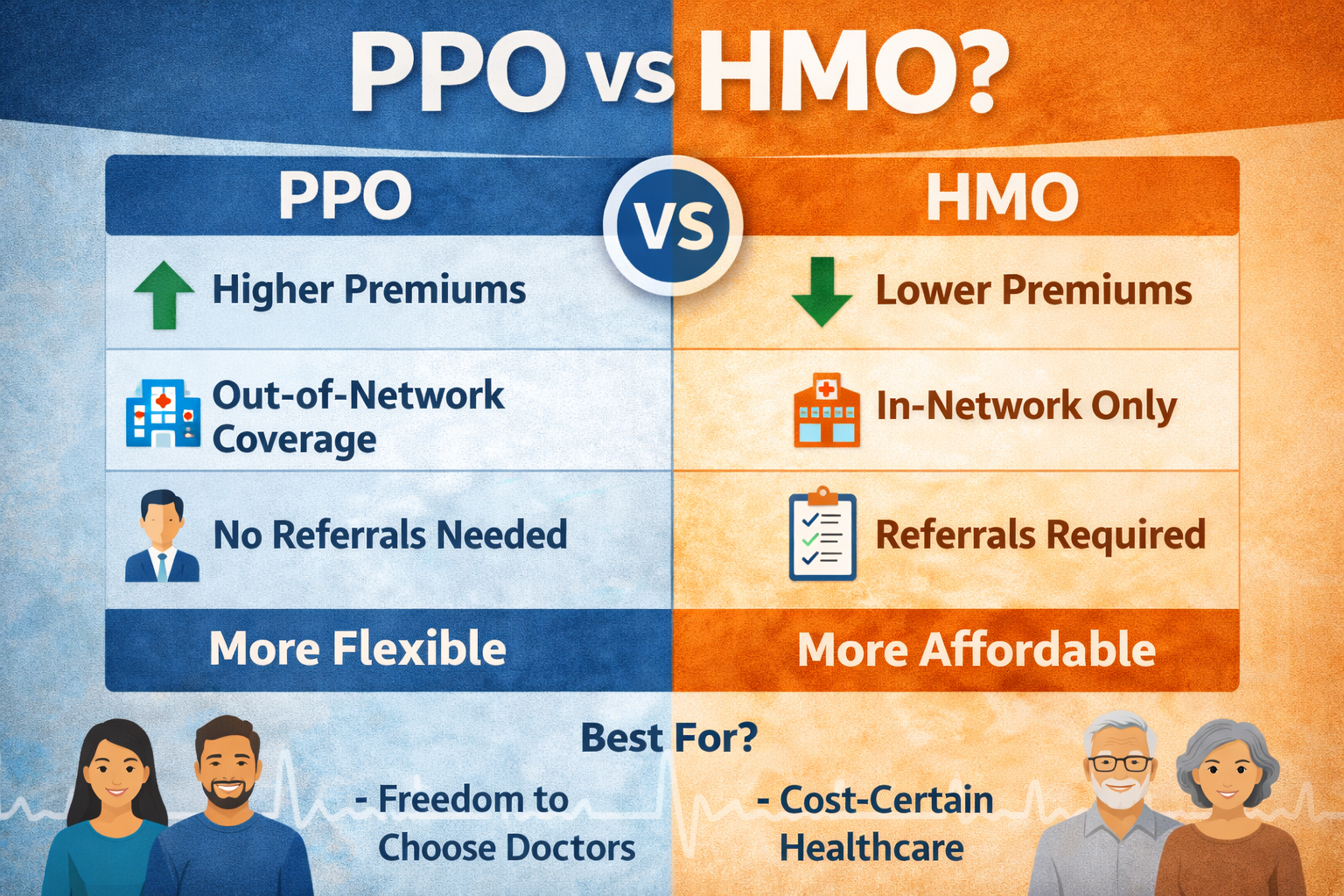
PPO vs HMO for Common Scenarios
Scenario 1: Healthy Individual, Rare Doctor Visits
Best choice: HMO
Why:
- Lower premiums
- Minimal care needs
- Predictable costs
Scenario 2: Chronic Condition or Specialist Care
Best choice: PPO
Why:
- Direct specialist access
- Larger network
- Fewer delays
Scenario 3: Self-Employed or Variable Income
Depends heavily on subsidies.
Related guide: ACA Subsidies for Self-Employed
Scenario 4: Young Adult Under 30
Often HMOs or catastrophic plans make sense.
Related guide: ACA Subsidies for Young Adults Under 30
PPO vs HMO for Families
Families should consider:
- Pediatrician availability
- Specialist referrals
- Hospital systems in network
- Ongoing care needs
HMOs work well when:
- Care is centralized
- Doctors are within one system
- Costs matter more than flexibility
PPOs work better when:
- Multiple specialists are involved
- Children have ongoing conditions
- Families travel or relocate
Hidden Costs People Overlook
Many people compare only monthly premiums. That's a mistake.
You should also compare:
- Deductibles
- Copays vs coinsurance
- Out-of-pocket maximums
- Prescription drug coverage
- Referral delays
A cheaper HMO premium can become more expensive if access limitations disrupt care.
PPO vs HMO Myths (Debunked)
Myth: PPOs are always better
Reality: Not if you don't use the flexibility
Myth: HMOs are bad insurance
Reality: They are efficient and cost-effective for many people
Myth: PPOs eliminate surprise bills
Reality: Out-of-network billing still happens
How to Choose the Right Plan (Step-by-Step)
- Estimate your household income
How to Estimate Your Income for ACA Subsidies - Check your subsidy eligibility
ACA Subsidy Calculator for 2026 - Compare total yearly cost, not just premiums
- Verify your doctors are in network
- Consider how often you use healthcare
Final Verdict: PPO vs HMO
There is no universally "better" option.
Choose an HMO if you want lower costs, predictable care, and simplicity.
Choose a PPO if you want flexibility, specialist access, and network freedom.
The best plan is the one that fits your income, healthcare usage, and subsidy eligibility — not the acronym.
Next Step: Run the Numbers
Before choosing, use a subsidy calculator to see your real costs:
Compare PPO vs HMO with Your Real Costs
Get personalized estimates based on your income, household size, and ZIP code. See which plan type saves you the most money.
Try the Calculator →